This article is dedicated to the Domain Name System or DNS server which is the heart of any enterprise network. DNS is mostly used to resolve host names to IP addresses and IP addresses to host names.
This tutorial focuses on:
- Installing DNS server role
- Configuring forward lookup zone
- Configuring reverse lookup zone
- Adding a host record in forward lookup zone
- Adding a PTR record in reverse lookup zone
Prerequisites
For DNS server to be configured, you should meet the following requirements:
- Administrator account has strong password
- At least one static IP is configured
- Current security updates from Windows Update are installed
- Firewall is turned off
Installing DNS Server Role
Step 1: From task bar, open server manager dashboard
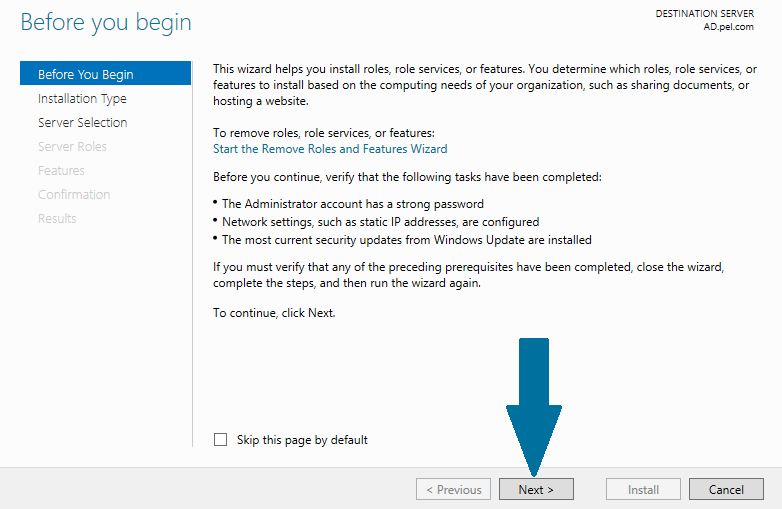
Step 2: Read the notes and meet the prerequisites. Click Next when you are done
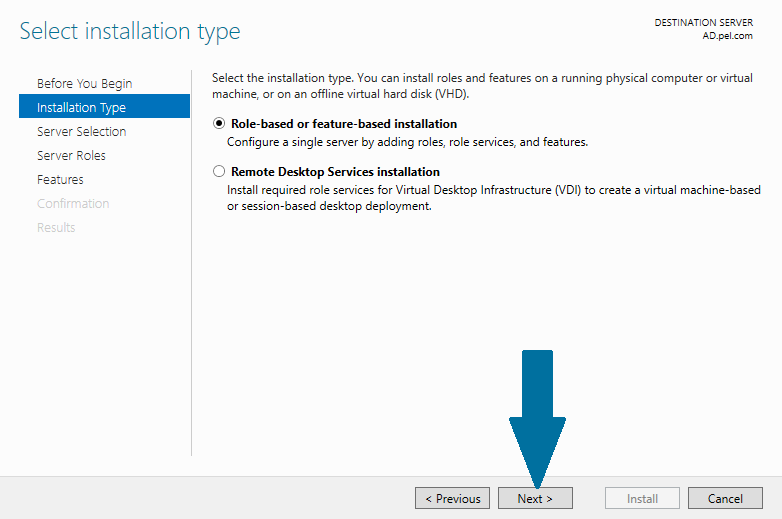
Step 3: Choose Role-based or feature-based installation and click Next
Figure 3
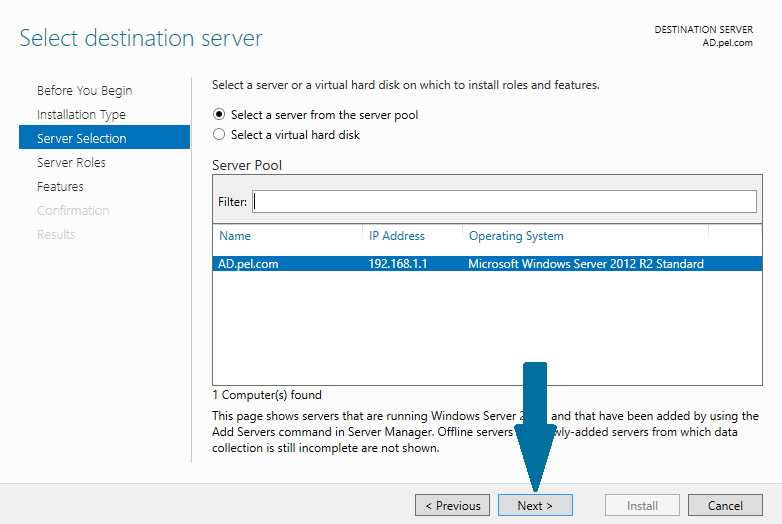
Step 4: Select the destination server from server pool on which you want to configure DNS and click Next
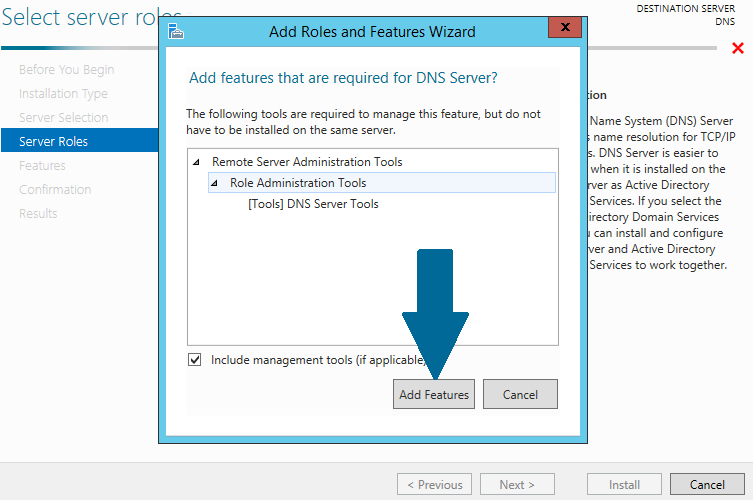
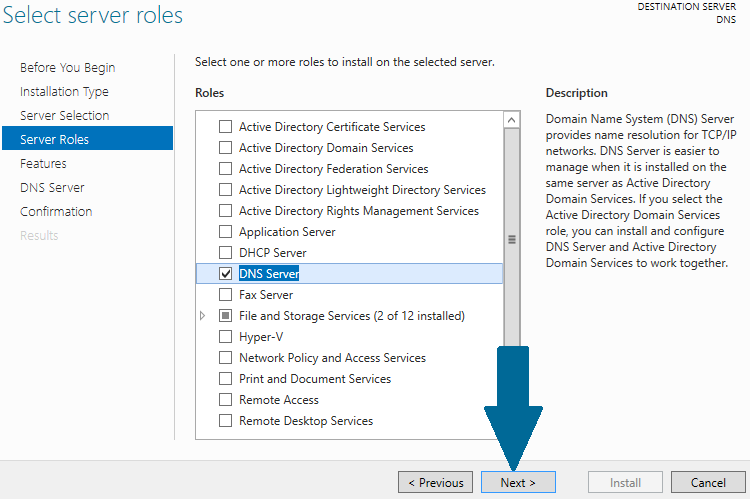
Step 5: Choose DNS Server from server roles. When prompted to install additional necessary features along with DNS server, click Add Features
Step 6: Click Next
Step 7: Keep default selections and click Next
Step 8: Read the important notes and click Next
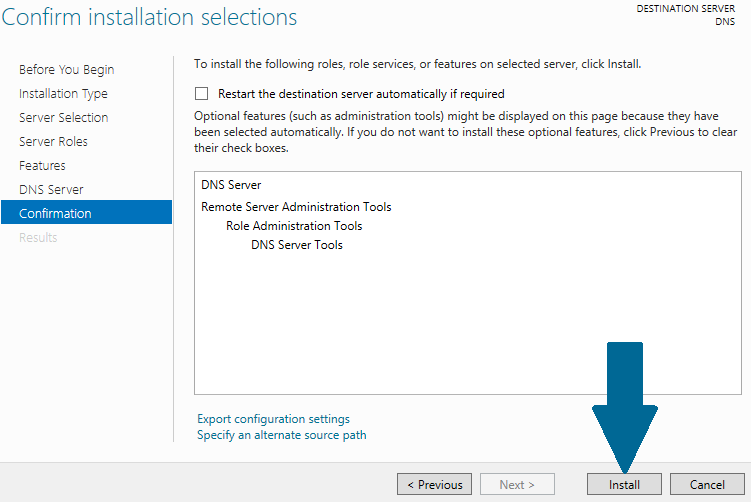
Step 9: Click Install. Wait for a moment before DNS role is installed
Configuring Forward Look Up Zone
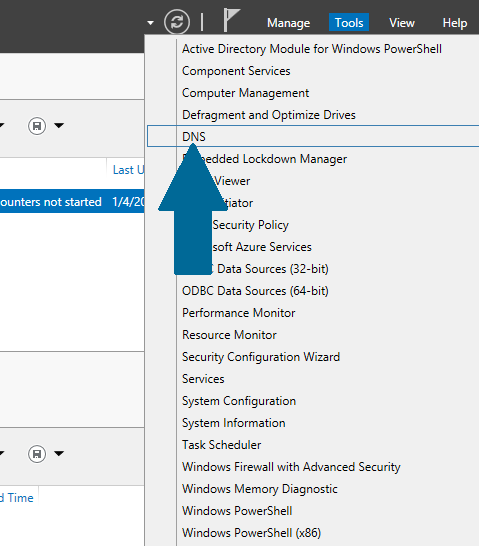
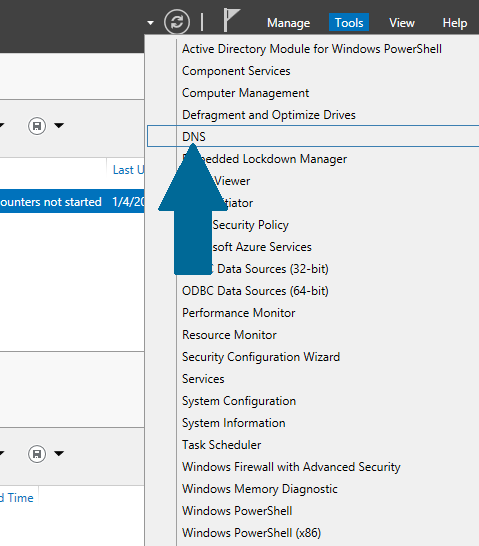
Step 1: Open server manager dashboard, and then open tools. Scroll to DNS and click it
Step 2: Right-click Forward Lookup Zones and click New Zone
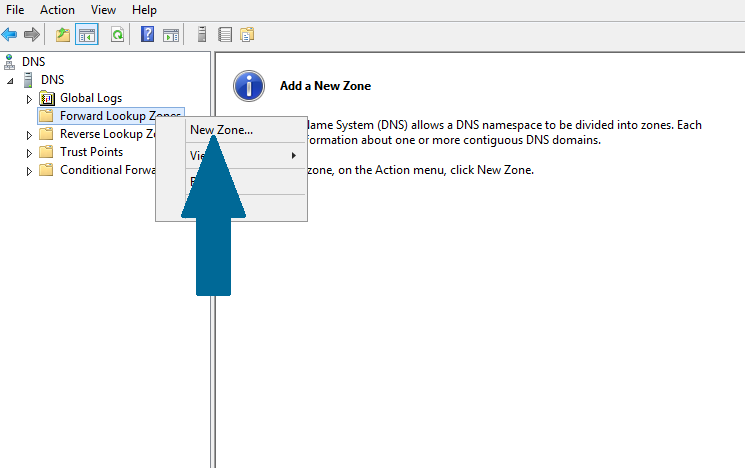 Figure 11
Figure 11
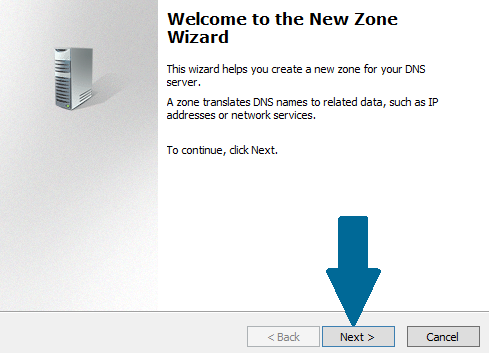
Step 3: Click Next
Figure 12
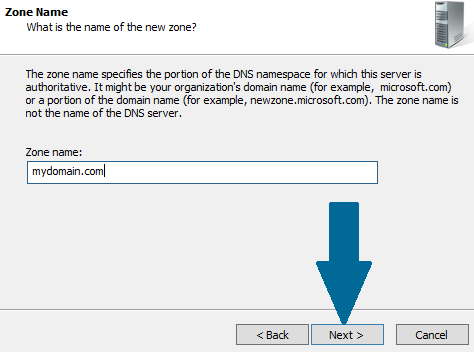
Step 4: Provide the zone name and click Next
Figure 13
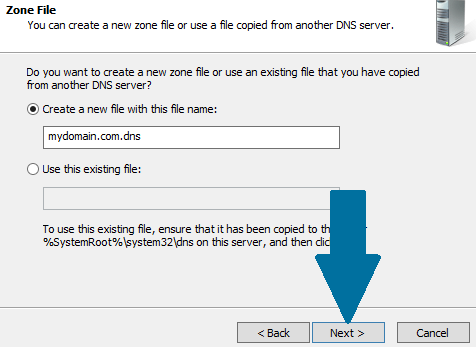
Step 5: Choose Create a new file with this file name and click Next
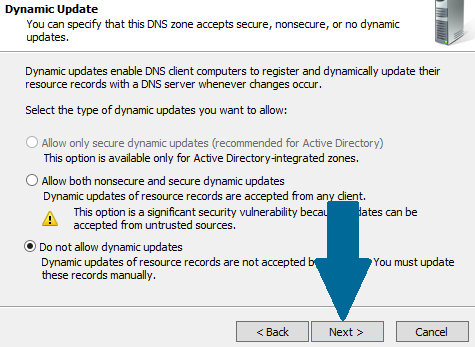
Step 6: Choose Do not allow dynamic updates and click Next
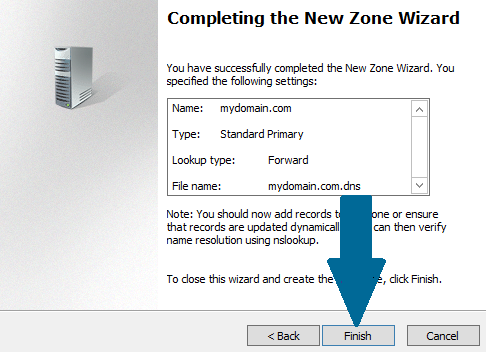
Step 7: Click Finish to successfully create the new zone
Configuring Reverse Look Up Zone
Step 1: Open server manager from task bar and click on Tools. Scroll to DNS and then click on it
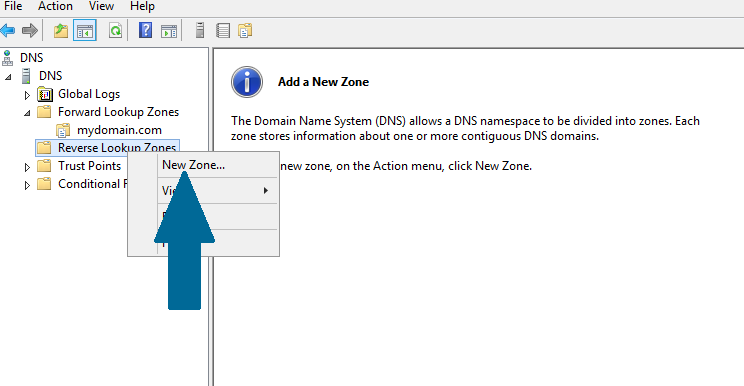
Step 2: Right-click Reverse Lookup Zones and then click New Zone
Step 3: Click Next
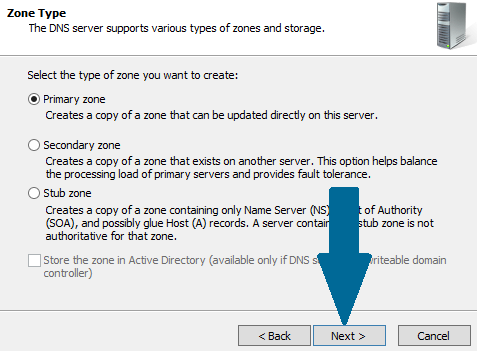
Step 4: Choose Primary zone and click Next
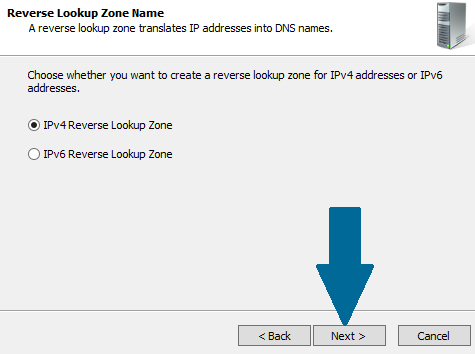
Step 5: Choose IPv4 Reverse Lookup Zone and click Next
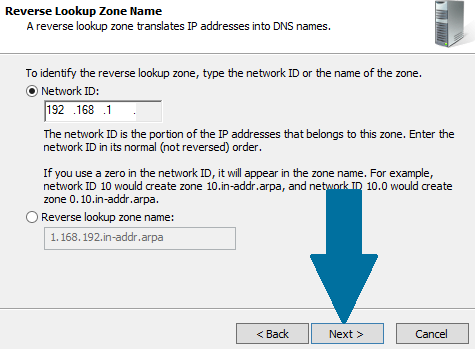
Step 6: Provide network ID and click Next
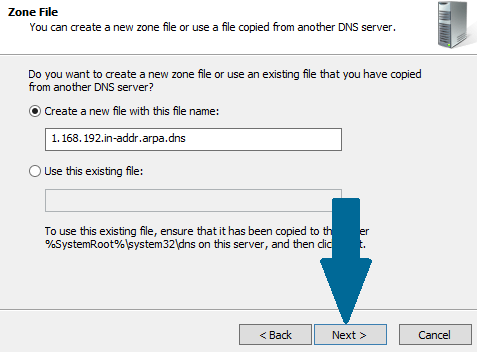
Step 7: Choose Create a new file with this file name: and click Next
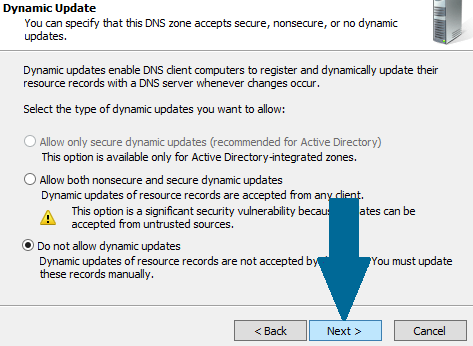
Step 8: Choose Do not allow dynamic updates and click Next
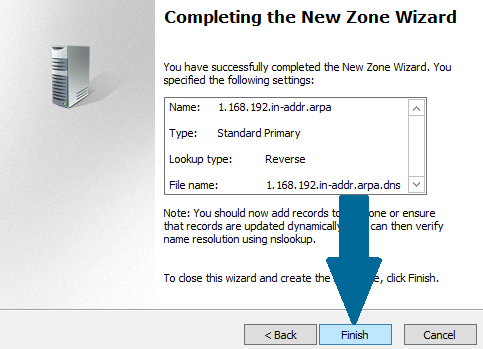
Step 9: Click Finish to end the wizard
Adding a New Host Record in Forward Look Up Zone
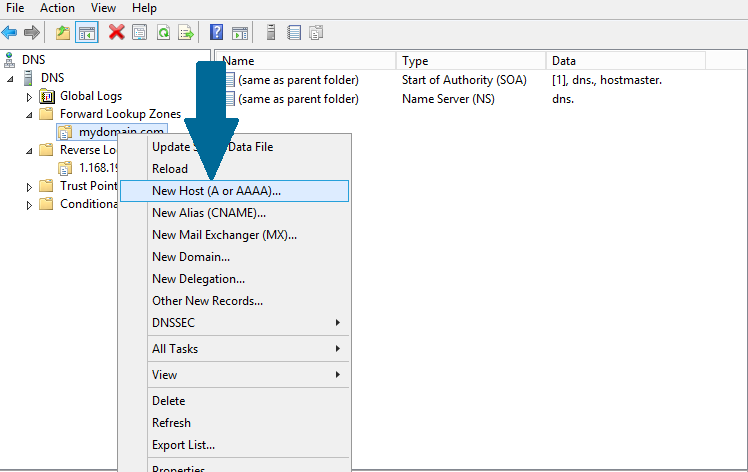
Step 1: Locate the zone in forward lookup zones and right-click on it. Scroll to New Host (A or AAAA) and click on it
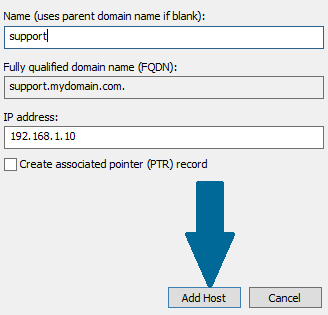
Step 2: Provide the name and click Add Host
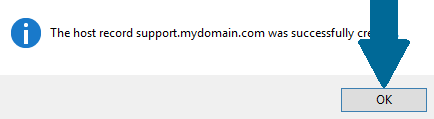
Step 3: Click OK and this new host record will be visible in zone
Adding a New PTR Record in Forward Look Up Zone
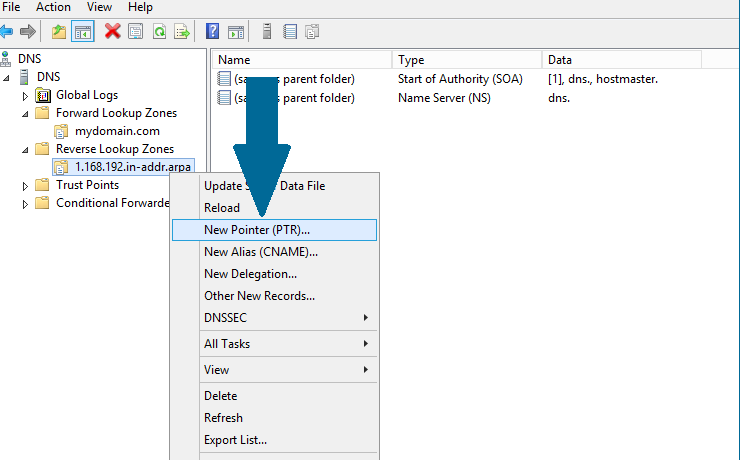
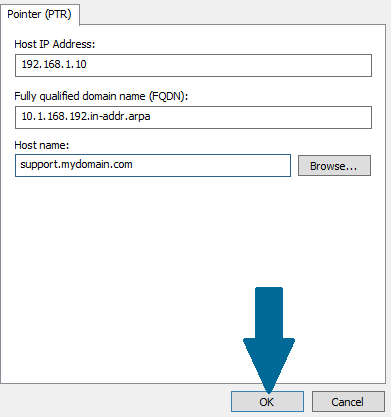
Step 1: Right-click the desired reverse lookup zone. Scroll to New Pointer (PTR)
Step 2: Provide host name and click OK
Conclusion
In this article, I have showed the steps which are used to configure DNS server on Windows Server 2012 R2. You can test this configuration by taking a DNS client and pointing its DNS setting to this server. You should be able to resolve the host you just created.